Mounjaro vs. Wegovy: Which Weight Loss Medication is Best for You?
Mounjaro and Wegovy are two of the most well-known weight loss medications, so we've created this guide to help you understand the difference between them, and whether there are any alternative treatments that may help you reach your weight loss goals.
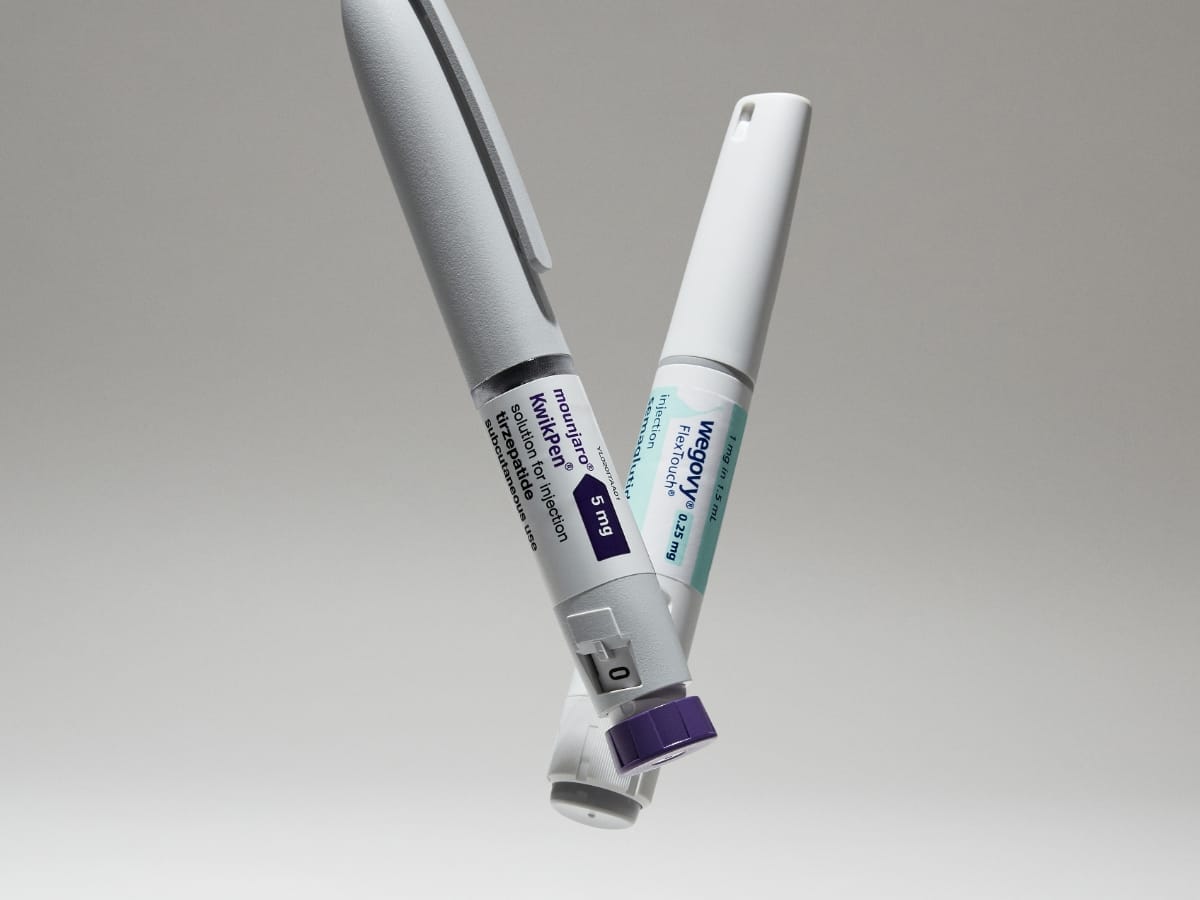
Trying a weight loss treatment can feel overwhelming. There are so many popular treatments available, and it can be hard to know which is best for you. Mounjaro and Wegovy are two of the most well-known weight loss medications, so we've created this guide to help you understand the difference between them, and whether there are any alternative treatments that may help you reach your weight loss goals.
About GLP-1 medications
Wegovy and Mounjaro are both injectable weight loss treatments. Wegovy is a GLP-1 (glugacon-like peptide-1) receptor agonist, and it works by mimicking the natural GLP-1 hormone in your body. GLP-1 is an incretin hormone, which means it's released into your gut after you eat. It encourages insulin production to help stabilise your blood sugar levels. This effect is why GLP-1 medications were originally developed as treatments for people with type-2 diabetes.
GLP-1s also target the hunger center in your brain to reduce your appetite and slow gastric emptying (the rate food leaves your stomach) which helps you feel full and reduce your food intake. [1] [2]
Mounjaro works in the same way, except it's a dual GIP (glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide) and GLP-1 receptor agonist. This simply means it mimics two incretin hormones instead of just GLP-1.
What is Mounjaro?
Mounjaro is a weight loss medication developed by the pharmaceutical company Eli Lilly. It contains the active ingredient tirzepatide, and it's unique because it's a dual agonist medication, targeting both GLP-1 and GIP receptors in the body. In simple terms, Mounjaro provides all the insulin release, appetite regulation and blood sugar control benefits of a GLP-1 medication, but its additional targeting of GIP receptors enhances these effects. [3]
What is Wegovy?
Wegovy contains the active ingredient semaglutide, a GLP-1 agonist. While some GLP-1 treatments were diabetes medications first, Wegovy was created as a dedicated weight loss drug. Semaglutide is found in other popular weight loss medications, including Ozempic, but Wegovy contains higher doses.
Similarities between Mounjaro and Wegovy
Both Mounjaro and Wegovy are clinically proven weight loss treatments that target areas of your gut and brain to reduce hunger and help you feel full. They're injectable medications that come in pre-filled pens you administer as subcutaneous injections, in the fatty layer just under your skin.
The eligibility criteria for both drugs is the same. For your healthcare provider to prescribe them, you must have a BMI of 30 or over. You may also qualify if your BMI is over 27 and you have a weight-related health condition, such as high blood pressure, diabetes, heart disease or raised cholesterol.
Differences between Mounjaro and Wegovy
There are also key differences between these two treatments.
How they work
Mounjaro and Wegovy contain different active ingredients which don't work in exactly the same way. Mounjaro has the extra benefit of dual GLP-1 and GIP action, while Wegovy is solely a GLP-1 agonist.
Average weight loss
Mounjaro and Wegovy both have proven effectiveness at aiding weight loss in clinical trials. Studies show Wegovy can help you lose 14.9% of your body weight over 68 weeks. [4]
However, Mounjaro has a higher average weight loss, with one clinical study finding it could reduce your weight by up to 20.9% over 72 weeks on the maximum dose. [5]
You get the best results from either medication by following your treatment plan alongside long-term lifestyle changes, including a healthy diet and increased physical activity.
FDA approval
Both medications are approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for different uses. Wegovy is approved to aid with long-term weight management, alongside a diet and exercise plan. Mounjaro is only approved to help improve blood sugar levels in adults with type-2 diabetes, but licensed healthcare providers can prescribe it off-label for weight loss.
Common side effects
With any medication, you may experience mild side effects, and these vary from person to person even if they're taking the same drug. This is no different with Mounjaro and Wegovy. The most common side effects people report are:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Constipation
- Diarrhoea
- Headaches
- Fatigue
- Stomach pain
- Injection site reactions (redness or itching)
Rarely, these injections can also cause more serious adverse effects, including pancreatitis (inflamed pancreas), acute kidney injury (reduced blood flow to kidneys caused by dehydration) and anaphylaxis (allergic reaction). If you experience any of these, dial 911 and seek urgent medical attention.
Want to try medicated weight loss?
Our clinicians assess your medical history and help you decide whether out treatment can help you on your weight loss journey.
Start an online consultation today.
References:
- Collins L, Costello RA. Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists [Internet]. PubMed. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK551568/
- Latif W, Lambrinos KJ, Rodriguez R. Compare And Contrast the Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists (GLP1RAs) [Internet]. PubMed. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK572151
- Nguyen TMD. Adiponectin: Role in Physiology and Pathophysiology. International Journal of Preventive Medicine [Internet]. 2020 Sep 3;11. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7554603
- Wilding JPH, Batterham RL, Calanna S. Once-Weekly Semaglutide in Adults with Overweight or Obesity. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2021 Feb 10;384(11):989–1002.
- Jastreboff AM, Aronne LJ, Ahmad NN, Wharton S, Connery L, Alves B, et al. Tirzepatide Once Weekly for the Treatment of Obesity. New England Journal of Medicine [Internet]. 2022 Jun 4;387(3). Available from: https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa2206038
